Anticoagulants are a class of drugs that work to prevent the coagulation (clotting) of blood. Such substances occur naturally in leeches and blood-sucking insects. A group of pharmaceuticals called anticoagulants can be used as an injection into human beings as a medication for thrombotic disorders. Oral anticoagulants are also available. Some anticoagulants are used in medical equipment, such as test tubes, blood transfusion bags, and renal dialysis equipment.
Medical uses
Anticoagulants reduce blood clotting which can help prevent deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke.
Therapeutic uses of anticoagulants include atrial fibrillation, pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, venous thromboembolism, congestive heart failure, stroke, myocardial infarction, and genetic or acquired hypercoagulability.
The decision to begin therapeutic anticoagulation often involves the use of multiple bleeding risk predictable outcome tools as non-invasive pre-test stratifications due to the potential for bleeds while on blood thinning agents. Among these tools are HAS-BLED, ATRIA, and CHA2DS2-VASc.
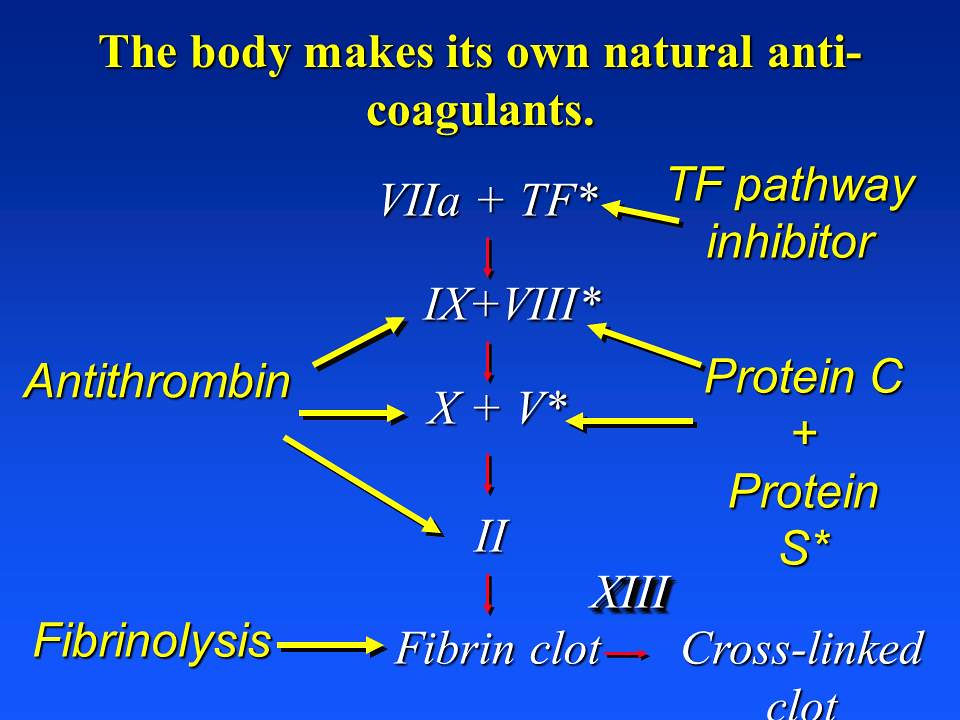
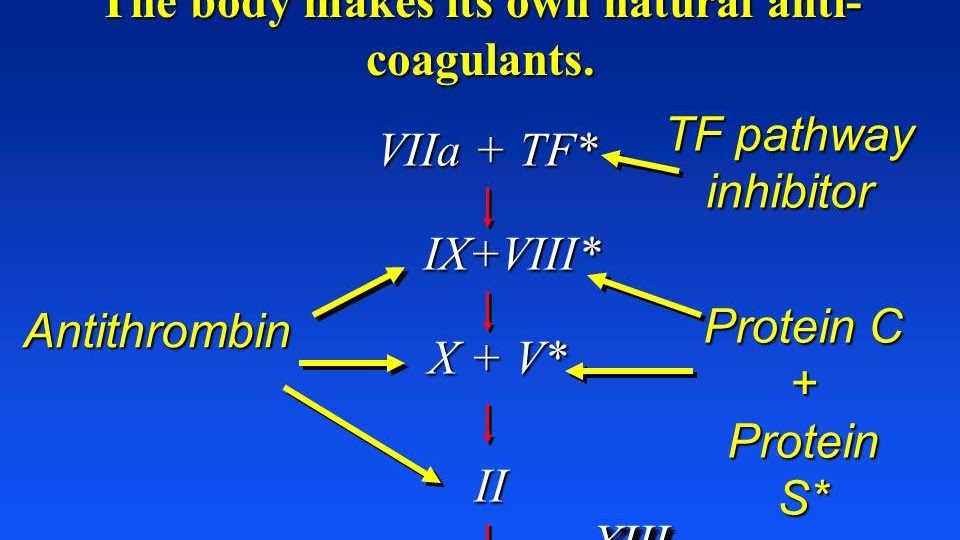
Natural Anticoagulants Video
Adverse effects
Patients aged 80 years or more may be especially susceptible to bleeding complications, with a rate of 13 bleeds per 100 person-years. These oral anticoagulants are used widely as poisons for mammalian pests, especially rodents. (For details, see rodenticide and warfarin.) Depletion of vitamin K by Coumadin therapy increases risk of arterial calcification and heart valve calcification, especially if too much vitamin D is present.
Interactions
Foods and food supplements with blood-thinning effects include nattokinase, lumbrokinase, beer, bilberry, celery, cranberries, fish oil, garlic, ginger, ginkgo, ginseng, green tea, horse chestnut, licorice, niacin, onion, papaya, pomegranate, red clover, soybean, St. John's wort, turmeric, wheatgrass, and willow bark. Many herbal supplements have blood-thinning properties, such as danshen and feverfew. Multivitamins that do not interact with clotting are available for patients on anticoagulants.
However, some foods and supplements encourage clotting. These include alfalfa, avocado, cat's claw, coenzyme Q10, and dark leafy greens such as spinach. Their intake should be avoided whilst taking anticoagulants or, if coagulability is being monitored, their intake should be kept approximately constant so that anticoagulant dosage can be maintained at a level high enough to counteract this effect without fluctuations in coagulability.
Grapefruit interferes with some anticoagulant drugs, increasing the amount of time it takes for them to be metabolized out of the body, and so should be eaten only with caution when on anticoagulant drugs.
Anticoagulants are often used to treat acute deep vein thrombosis. People using anticoagulants to treat this condition should avoid using bed rest as a complementary treatment because there are clinical benefits to continuing to walk and remaining mobile while using anticoagulants in this way. Bed rest while using anticoagulants can harm patients in circumstances in which it is not medically necessary.

Types
The novel oral anticoagulants (NOACs) including dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and apixaban have been shown to be as good or better than the coumarins (vitamin K antagonists) with less serious side effects. The newer anticoagulants (NOACs), are more expensive than the traditional ones and should be used with care in patients with kidney problems. Additionally, there is no antidotum yet, so it is difficult to stop their effects in the body in cases of emergency (accidents, urgent surgery). Good adherence to this therapy is of paramount importance for optimal effect.
Coumarins (vitamin K antagonists)
These oral anticoagulants are derived from coumarin, which is found in many plants. A prominent member of this class is warfarin (Coumadin). It takes at least 48 to 72 hours for the anticoagulant effect to develop. Where an immediate effect is required, heparin must be given concomitantly. These anticoagulants are used to treat patients with deep-vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE) and to prevent emboli in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF), and mechanical prosthetic heart valves. Other examples are acenocoumarol and phenprocoumon, atromentin and phenindione.
The coumarins brodifacoum and difenacoum are used as rodenticides, but are not used medically.
Heparin and derivative substances
Heparin is a biological substance, usually made from pig intestines. It works by activating antithrombin III, which blocks thrombin from clotting blood. Heparin can be used in vivo (by injection), and also in vitro to prevent blood or plasma clotting in or on medical devices. In venipuncture, Vacutainer brand blood collecting tubes containing heparin usually have a green cap.
Low molecular weight heparin
Low molecular weight heparin, a more highly processed product, is useful as it does not require monitoring of the APTT coagulation parameter (it has more predictable plasma levels) and has fewer side effects.
Synthetic pentasaccharide inhibitors of factor Xa
- Fondaparinux is a synthetic sugar composed of the five sugars (pentasaccharide) in heparin that bind to antithrombin. It is a smaller molecule than low molecular weight heparin.
- Idraparinux
Direct factor Xa inhibitors
Drugs such as rivaroxaban, apixaban and edoxaban work by inhibiting factor Xa directly (unlike the heparins and fondaparinux, which work via antithrombin activation). Also betrixaban (LY517717) from Portola Pharmaceuticals, darexaban (YM150) from Astellas and more recent TAK-442 letaxaban (Takeda) and eribaxaban (PD0348292) (Pfizer). The development of darexaban was discontinued in September 2011: in a trial for prevention of recurrences of myocardial infarction in top of dual antiplatelet therapy, the drug did not demonstrate effectiveness and the risk of bleeding was increased by approximately 300%. The development of letaxaban was discontinued for acute coronary syndrome in May 2011 following negative results from a Phase II study.
Direct thrombin inhibitors
Another type of anticoagulant is the direct thrombin inhibitor. Current members of this class include the bivalent drugs hirudin, lepirudin, and bivalirudin; and the monovalent drugs argatroban and dabigatran. An oral direct thrombin inhibitor, ximelagatran (Exanta) was denied approval by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in September 2004 [1] and was pulled from the market entirely in February 2006 after reports of severe liver damage and heart attacks. [2] In November 2010, dabigatran was approved by the FDA to treat atrial fibrillation.
Antithrombin protein therapeutics
The antithrombin protein itself is used as a protein therapeutic that can be purified from human plasma or produced recombinantly (for example, Atryn, which is produced in the milk of genetically modified goats.)
Antithrombin is approved by the FDA as an anticoagulant for the prevention of clots before, during, or after surgery or birthing in patients with hereditary antithrombin deficiency.
Other types of anticoagulants
Many other anticoagulants exist, for use in research and development, diagnostics, or as drug candidates.
- Batroxobin, a toxin from a snake venom, clots platelet-rich plasma without affecting platelet functions (lyses fibrinogen).
- Hementin is an anticoagulant protease from the salivary glands of the giant Amazon leech, Haementeria ghilianii.

Society and culture
Warfarin (Coumadin) is the main agent used in the US and UK. Acenocoumarol and phenprocoumon are used more commonly outside the US and the UK.
Laboratory use
Laboratory instruments, blood transfusion bags, and medical and surgical equipment will get clogged up and become nonoperational if blood is allowed to clot. In addition, test tubes used for laboratory blood tests will have chemicals added to stop blood clotting. Apart from heparin, most of these chemicals work by binding calcium ions, preventing the coagulation proteins from using them.
- Ethylene Diamine Tetra Acetic Acid (EDTA) strongly and irreversibly chelates (binds) calcium ion to prevent blood from clotting.
- Citrate is in liquid form in the tube and is used for coagulation tests, as well as in blood transfusion bags. It binds the calcium, but not as strongly as EDTA. Correct proportion of this anticoagulant to blood is crucial because of the dilution, and it can be reversed with the addition of calcium. It can be in the form of sodium citrate or acid-citrate-dextrose.
- Oxalate has a mechanism similar to that of citrate. It is the anticoagulant used in fluoride oxalate tubes used to determine glucose and lactate levels.
Are You Looking for Products
Here some products related to "Anticoagulant".
Amazon.com : Glucosamine ..
Captains Krill Oil (2-pac..
Terry Naturally Curamin, ..
BioSil - Bone Collagenize..
Get these at Amazon.com* amzn.to is official short URL for Amazon.com, provided by Bitly
Source of the article : here



1 komentar:
Warfarin belongs to the class of medications called anticoagulants. It is sometimes referred to as a "blood thinner," although it does not actually thin the blood. Warfarin helps to prevent blood clots from forming or from getting bigger, but it does not dissolve blood clots. Warfarin is used for the treatment of blood clots in the veins, arteries, lungs, and heart. It is also used to prevent clots for people with conditions that put them at an increased risk of developing blood clots (e.g., some abnormal heart rhythms (atrial fibrillation), leg circulation problems). It is also used to reduce the risk of blood clots due to surgical procedures or trauma.
Blood clots in the circulation are dangerous because they can cause medical problems such as heart attacks, stroke, and pulmonary embolism. Warfarin helps to reduce blood clotting within 24 hours of taking the medication. The full effect may take 72 to 96 hours to occur.
Source: Best Canadian Prescription Drugs
EmoticonEmoticon